Berechnen Sie den Abstand von \(g\) und \(h\).
(1 BE)
Lösung zu Teilaufgabe b
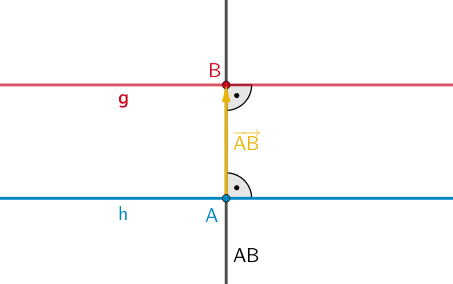
Planskizze (optional): Der Abstand zwischen der Gerade \(\textcolor{#cc071e}{g}\) und der parallelen Gerade \(\textcolor{#0087c1}{h}\) ist gleich dem Betrag des Verbindungsvektors \(\textcolor{#e9b509}{\overrightarrow{AB}}\).
\(\textcolor{#0087c1}{A2|0|0(}\), \(\textcolor{#cc071e}{B(-2|3|2)}\) (vgl. Teilaufgabe a)
Betrag eines Vektors
\[ \vert \overrightarrow{a} \vert = \sqrt{\overrightarrow{a} \circ \overrightarrow{a}} = \sqrt{{a_1}^2 + {a_2}^2 + {a_3}^2}\]
(vgl. Merkhilfe)
\[\begin{align*} d(\textcolor{#cc071e}{g};\textcolor{#0087c1}{h}) &= \vert \textcolor{#e9b509}{\overrightarrow{AB}} \vert = \vert \textcolor{#cc071e}{\overrightarrow{B}} - \textcolor{#0087c1}{\overrightarrow{A}} \vert \\[0.8em] &= \left| \textcolor{#cc071e}{\begin{pmatrix} -2 \\ 3 \\ 2 \end{pmatrix}} - \textcolor{#0087c1}{\begin{pmatrix} 2 \\ 0 \\ 0 \end{pmatrix}} \right| = \left| \begin{pmatrix} -4 \\ 3 \\ 2 \end{pmatrix} \right| \\[0.8em] &= \sqrt{(-4)^{2} + 3^{2} + 2^{2}} = \sqrt{29} \end{align*}\]

