Die in \(\mathbb R\) definierte Funktion \(F \colon x \mapsto -5(x+1)\cdot e^{-x}\) ist eine Stammfunktion von \(f\). Berechnen Sie mit dem Term aus Aufgabe 1d den Flächeninhalt der Figur auf eine Nachkommastelle genau.
(3 BE)
Lösung zu Teilaufgabe 1e
\(F(x) = -5(x+1)\cdot e^{-x}; \; D_F = \mathbb R\)
\(\displaystyle 2 \cdot \left( (5 - \ln{5}) \cdot \ln{5} - \int_{\ln{5}}^5 f(x)dx\right)\) (Term aus Teilaufgabe 1d)

\[\int_a^b f(x)dx = \left[ F(x) \right]_a^b = F(b) - F(a)\]
Dabei ist \(F\) eine Stammfunktion von \(f\).
Die Berechnung eines bestimmten Integrals hängt maßgeblich davon ab, wie schwierig es ist, eine Stammfunktion des Integranden zu bilden.
Nachfolgend sind in diesem Zusammenhang wichtige unbestimmte Integrale aufgeführt (\(C \in \mathbb R\)):
\[\int x^{r} dx = \frac{x^{r + 1}}{r + 1} + C \quad (r \neq - 1)\]
\[\int \frac{1}{x}\,dx = \ln{\vert x \vert} + C\]
\[\int \sin{x} \, dx = -\cos{x} + C\]
\[\int \cos{x} \, dx = \sin{x} + C\]
\[\int e^{x} dx = e^{x} + C\]
\[\int \ln{x}\, dx = -x + x \cdot \ln{x} + C\]
\[\int \frac{f'(x)}{f(x)} dx = \ln{\vert f(x) \vert} + C\]
\[\int f'(x) \cdot e^{f(x)} dx = e^{f(x)} + C\]
\(\displaystyle \int f(ax + b) \, dx = \frac{1}{a} \cdot F(ax + b) + C\), wobei \(F\) eine Stammfunktion von \(f\) ist.
Ein bestimmtes Integral \(\displaystyle \int_a^b f(x)dx\) gibt die Flächenbilanz der Inhalte der Flächen an, die der Graph der Funktion \(f\) im Intervall \([a;b]\) mit der \(x\)-Achse einschließt.
Dabei zählen für \(a < b\) Flächen oberhalb der \(\textcolor{#0087c1}{x}\)-Achse positiv und Flächen unterhalb der \(\textcolor{#cc071e}{x}\)-Achse negativ. Für \(a > b\) zählen die Flächen mit umgekehrten Vorzeichen.
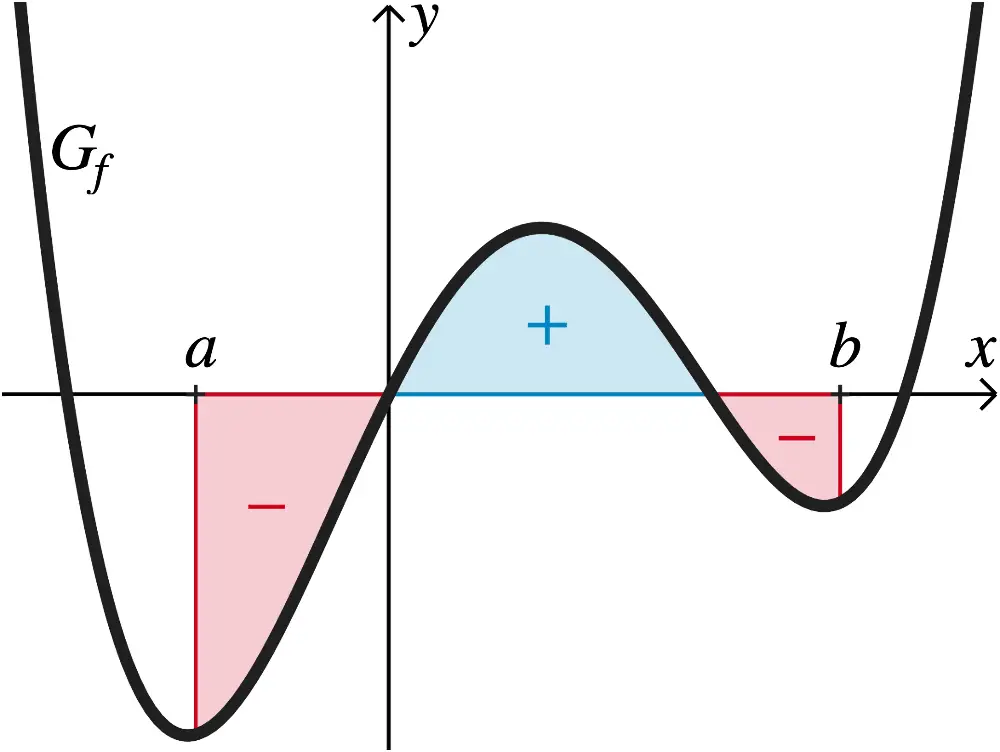
Identische Integrationsgrenzen:
\[\int_{\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}^{\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}f(x)dx = 0\]
Faktorregel:
\(\displaystyle \int_{a}^{b} \textcolor{#e9b509}{k} \cdot f(x)dx = \textcolor{#e9b509}{k} \cdot \int_{a}^{b}f(x)dx\) mit \(\textcolor{#e9b509}{k} \in \mathbb R\)
Summenregel:
\[\int_{a}^{b} \left[f(x) \pm g(x) \right] dx = \int_{a}^{b}f(x)\,dx \pm \int_{a}^{b}g(x)\,dx\]
Vertauschungsregel:
\[\int_{\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}^{\textcolor{#0087c1}{b}}f(x)\,dx = -\int_{\textcolor{#0087c1}{b}}^{\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}f(x)\,dx\]
Zerlegung in Teilintervalle:
\[\displaystyle \int_{\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}^{\textcolor{#0087c1}{b}}f(x)\,dx = \int_{\textcolor{#cc071e}{a}}^{\textcolor{#89ba17}{c}}f(x)\,dx + \int_{\textcolor{#89ba17}{c}}^{\textcolor{#0087c1}{b}}f(x)\,dx\]
\[\begin{align*}A_{\text{Figur}} &=2 \cdot \left( (5 - \ln{5}) \cdot \ln{5} - \int_{\textcolor{#cc071e}{\ln{5}}}^{\textcolor{#0087c1}{5}} f(x)dx\right) \\[0.8em] &= 2 \cdot \Big( (5 - \ln{5}) \cdot \ln{5} - \big(F(\textcolor{#0087c1}{5}) - F(\textcolor{#cc071e}{\ln{5}})\big)\Big) \\[0.8em] &= 2 \cdot \Bigg((5 - \ln{5}) \cdot \ln{5} - \bigg(-5(\textcolor{#0087c1}{5}+1) \cdot e^{-\textcolor{#0087c1}{5}} - \Big( -5(\textcolor{#cc071e}{\ln{5}} + 1) \cdot e^{-\textcolor{#cc071e}{\ln{5}}} \Big)\bigg) \Bigg) &&\Big| \; e^{-\ln{5}} = e^{\ln{\left(5^{-1}\right)}} = e^{\ln{\left(\frac{1}{5}\right)}} = \frac{1}{5} \\[0.8em] &= 2 \cdot \left( (5 - \ln{5}) \cdot \ln{5} + \frac{30}{e^5} - (\ln{5} + 1)\right) \\[0.8em] &\approx 6{,}1\end{align*}\]